Human PARVA / Actopaxin Protein (GST Tag)
CH-ILKBP,MXRA2
- 100ug (NPP2384) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13919-H09E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | CH-ILKBP,MXRA2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PARVA /GST chimera consists of 606 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 69.4 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 69 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 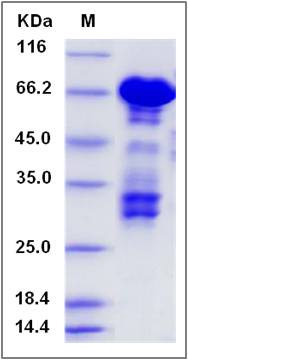 |
| Purity | > 60 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human PARVA (Q9NVD7-1) (Met1-Glu372) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Extracellular Matrix |Structures |Focal Adhesions | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Actopaxin, also known as alpha-parvin, belongs to the parvin family. It is widely expressed, with highest levels in heart, skeletal muscle, kidney and liver. Actopaxin contains 2 CH (calponin-homology) domains and probably plays a role in the regulation of cell adhesion and cytoskeleton organization. It interacts with integrin-linked protein kinase and probably with actin and the LD1 and LD4 motifs of PXN. Actopaxin binds directly to both F-actin and paxillin LD1 and LD4 motifs. Actopaxin also exhibits robust focal adhesion localization in several cultured cell types but is not found along the length of the associated actin-rich stress fibers. It is absent from actin-rich cell-cell adherens junctions. |
| Reference |
