Human PD1 / PDCD1 Protein (His & Fc Tag)
CD279,hPD-1,hPD-l,hSLE1,PD-1,PD1,SLEB2
- 100ug (NPP4148) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10377-H03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD279,hPD-1,hPD-l,hSLE1,PD-1,PD1,SLEB2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PD1/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer consists of 390 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 44 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rhPD1/Fc monomer migrates as an approximately 60-65 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 32 |
| SDS-PAGE | 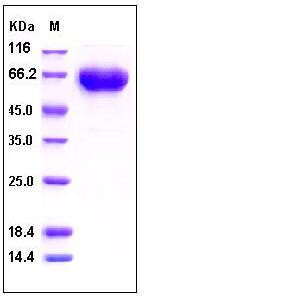 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Gln 167) of human PD1 (NP_005009.2) was fused with the C-terminal polyhistidine-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA . Immobilized recombinant human PD-L2 at 1 μg/ml (100ul/well) can bind human PD1 / Fc chimera with a linear range of 7.8-1000 ng/ml . |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Programmed cell death 1, also known as PDCD1, is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein, and is an immunoreceptor belonging to the CD28/CTLA-4 family negatively regulates antigen receptor signaling by recruiting protein tyrosine phosphatase, SHP-2 upon interacting with either of two ligands, PD-L1 or PD-L2. PD1 inhibits the T-cell proliferation and production of related cytokines including IL-1, IL-4, IL-10 and IFN-γ by suppressing the activation and transduction of PI3K/AKT pathway. In addition, coligation of PD1 inhibits BCR-mediating signal by dephosphorylating key signal transducer. PD1 has been suggested to be involved in lymphocyte clonal selection and peripheral tolerance, and thus contributes to the prevention of autoimmune diseases. Furthermore, PD1 is shown to be a regulator of virus-specific CD8+ T cell survival in HIV infection. As a cell surface molecule, PDCD1 regulates the adaptive immune response. Engagement of PD-1 by its ligands PD-L1 or PD-L2 transduces a signal that inhibits T-cell proliferation, cytokine production, and cytolytic function. |
| Reference |
