Human PDE1B Protein (His & GST Tag)
PDE1B1,PDES1B
- 100ug (NPP2386) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11746-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | PDE1B1,PDES1B |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PDE1B/GST chimera consists of 773 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 89.2 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 75 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 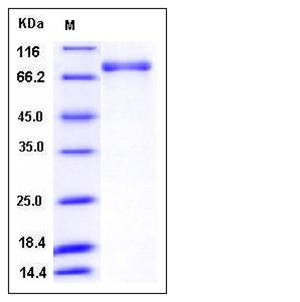 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PDE1B long isoform (Q01064-1) (Met 1-Asp 536) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Second Messenger |Nucleotide Messenger |cGMP |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent 3',5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1B, also known as Cam-PDE 1B and PDE1B, is a cytoplasm protein which belongs to the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family and PDE1 subfamily. Phosphodiesterase-10A (PDE10A), Phosphodiesterase-1B (PDE1B), Phosphodiesterase-4B (PDE4B), and Phosphodiesterase-4A (PDE4A) are important regulators of signal transduction in striatum due to their catalysis of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. PDE1B is highly expressed in the striatum. It binds two divalent metal cations per subunit. Site one of PDE1B may preferentially bind zinc ions, while site two of PDE1B has a preference for magnesium and/or manganese ions. PDE1B is a cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase with a dual-specificity for the second messengers cAMP and cGMP, which are key regulators of many important physiological processes. It has a preference for cGMP as a substrate. |
| Reference |
