Human PDE4B / DPDE4 Protein (His & GST Tag)
DPDE4,PDEIVB
- 100ug (NPP4151) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11527-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | DPDE4,PDEIVB |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PDE4B/GST chimera consists of 801 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 92.2 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 100 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 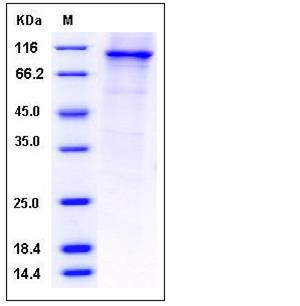 |
| Purity | > 80 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PDE4B isofrom 2 (NP_001032416.1) (Met 1-Thr 564) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Second Messenger |Nucleotide Messenger |cAMP |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 0.5mM GSH, 10% gly, 0.5mM PMSF, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4B, also known as PDE4B and DPDE4, is a member of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family. PDE4 subfamily. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs) comprise a large family of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of cAMP or cGMP and are implicated in various diseases. The crystal structures reveal a common scheme of inhibitor binding to the PDEs: (i) a hydrophobic clamp formed by highly conserved hydrophobic residues that sandwich the inhibitor in the active site; (ii) hydrogen bonding to an invariant glutamine that controls the orientation of inhibitor binding. A scaffold can be readily identified for any given inhibitor based on the formation of these two types of conserved interactions. These structural insights will enable the design of isoform-selective inhibitors with improved binding affinity and should facilitate the discovery of more potent and selective PDE inhibitors for the treatment of a variety of diseases. PDE4B / DPDE4 hydrolyzes the second messenger cAMP, which is a key regulator of many important physiological processes. It is expressed in brain, heart, lung and skeletal muscle. PDE4B / DPDE4 may be involved in mediating central nervous system effects of therapeutic agents ranging from antidepressants to antiasthmatic and anti-inflammatory agents |
| Reference |
