Human PDE9A Protein (His Tag)
HSPDE9A2
- 100ug (NPP4152) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11745-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | HSPDE9A2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PDE9A consisting of 337 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 40 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 37 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 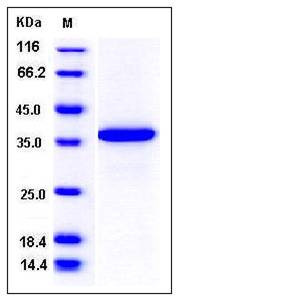 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PDE9A (O76083-2) C-terminal segment (Pro 181-Lys 506) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Second Messenger |Nucleotide Messenger |cAMP |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | High affinity cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9A, also known as PDE9A, is a member of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family and PDE9 subfamily. PDE9A is expressed in all tissues examined (testis, brain, small intestine, skeletal muscle, heart, lung, thymus, spleen, placenta, kidney, liver, pancreas, ovary and prostate) except blood. Highest levels of PDE9A is in brain, heart, kidney, spleen, prostate and colon. Isoform PDE9A12 is found in prostate. PDE9A mRNA is widely distributed throughout the rat and mouse brain, with the highest expression observed in cerebellar Purkinje cells. PDE9A is the only cGMP-specific PDE with significant expression in the forebrain, and as such is likely to play an important role in NO-cGMP signaling. PDE9A is highly conserved between species and is widely distributed throughout the rodent brain. PDE9A is probably involved in maintenance of low cGMP levels in cells and might play an important role in a variety of brain functions involving cGMP-mediated signal transduction. PDE9A hydrolyzes the second messenger cGMP, which is a key regulator of many important physiological processes. PDE9A represents a novel drug target worthy of further study. |
| Reference |
