Human PDHA1 / C54G1 Protein (aa 30-390, His & GST Tag)
PDHA,PDHAD,PDHCE1A,PHE1A
- 100ug (NPP2388) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14567-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | PDHA,PDHAD,PDHCE1A,PHE1A |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PDHA1/GST chimera consists of 598 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 68 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 65 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 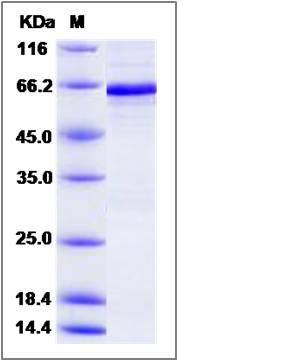 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PDHA1 (P08559-1) (Phe30-Ser390) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Cell cycle |Markers |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM Nacl, 3mM DTT, 10% gly, pH 8.0. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | PDHA1, also known as C54G1, is an alpha subunit of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Pyruvate dehydrogenase, together with dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase and lipoamide dehydrogenase, composes the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex. The PDH complex is a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial multienzyme complex that catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2), and provides the primary link between glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. PDHA1 plays a key role in the function of the PDH complex. Defects in PDHA1 can cause pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-alpha deficiency. Defects in PDHA1 also are the cause of X-linked Leigh syndrome (X-LS). X-LS is an early-onset progressive neurodegenerative disorder with a characteristic neuropathology consisting of focal, bilateral lesions in one or more areas of the central nervous system, including the brainstem, thalamus, basal ganglia, cerebellum, and spinal cord. |
| Reference |
