Human PFK2 / PFKFB3 Protein (His & GST Tag)
IPFK2,PFK2
- 100ug (NPP4166) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13230-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | IPFK2,PFK2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PFKFB3 /GST chimera consists of 757 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 87.4 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 75 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 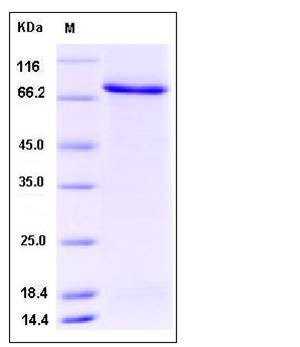 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PFKFB3 isoform 1 (Q16875-1) (Met 1-His 520) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Kinase activity untested |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Kinase |Intracellular Kinase |Other Intracellular Protein Kinases |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.0, 10% glycerol, 0.3mM DTT 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3, also known as 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase or PFK2 or PFKFB3, is a potent activator of phosphofructokinase, which is a rate-limiting enzyme of glycolysis. Highly phosphorylated PFKFB3 protein was found in human tumor cells, vascular endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (Fru-2,6-BP) is an allosteric activator of 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase (PFK-1), a rate-limiting enzyme and essential control point in glycolysis. The concentration of PFK2 depends on the activity of the bifunctional enzyme, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase / fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFK-2 / FBPase). PFK2 controls the glycolytic flux via the allosteric activator fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Because of its proto-oncogenic character, the PFK-2/FBPase-2 of the PFKFB3 gene is assumed to play a critical role in tumorigenesis. The hypoxia-inducible form of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase / fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFKFB3) plays a crucial role in the progression of cancerous cells by enabling their glycolytic pathways even under severe hypoxic conditions. |
| Reference |
