Human PHKG1 Protein (GST Tag)
PHKG
- 100ug (NPP2404) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11034-H09B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | PHKG |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PHKG1/GST chimera consists of 612 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 71.3 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 65 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 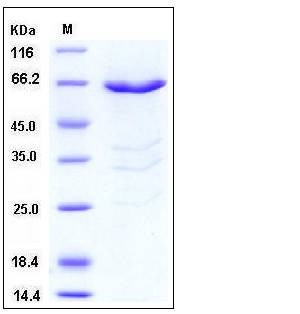 |
| Purity | > 87 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PHKG1 (NP_006204.1) (Met 1-Tyr 387) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | No Kinase Activity |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Cancer |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 0.5mM GSH, 0.5mM PMSF, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Phosphorylase b kinase gamma catalytic chain, skeletal muscle isoform, also known as Phosphorylase kinase subunit gamma-1 and PHKG1, is a member of the protein kinase superfamily and CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family. PHKG1 is the catalytic member of a 16 subunit protein kinase complex which contains equimolar ratios of 4 subunit types. The complex is a crucial glycogenolytic regulatory enzyme. Muscle glycogenosis caused by phosphorylase kinase (Phk) deficiency may lead to exercise intolerance, weakness and musculatur atrophy. The gene encoding the muscle isoform of the Phk gamma subunit (gamma M) is one of the candidate genes in which mutations responsible for this condition should be sought. Muscle-specific deficiency of Phk causes glycogen storage disease, clinically manifesting in exercise intolerance with early fatiguability, pain, cramps and occasionally myoglobinuria. |
| Reference |
