Human PHYH Protein
LN1,LNAP1,PAHX,PHYH1,RD
- 100ug (NPP2407) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13368-HNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | LN1,LNAP1,PAHX,PHYH1,RD |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PHYH consists of 309 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 35.6 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 26-32 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 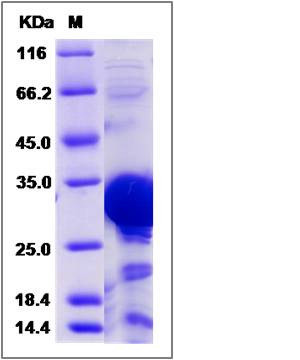 |
| Purity | > 80 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PHYH (O14832) (Ser31-Leu338) was expressed, with a N-terminal Met. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolic signaling pathways |Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM mops, 10% glycerol, 2mM DDT, 1mM EDTA, 0.2mM PMSF, 0.2M NaCl, pH 7.2 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | PHYH belongs to the family of iron(II)-dependent oxygenases, which typically incorporate one atom of dioxygen into the substrate and one atom into the succinate carboxylate group. PHYH is expressed in liver, kidney, and T-cells, but not in spleen, brain, heart, lung and skeletal muscle. It converts phytanoyl-CoA to 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA. Defects in PHYH can cause Refsum disease (RD). RD is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized clinically by a tetrad of abnormalities: retinitis pigmentosa, peripheral neuropathy, cerebellar ataxia, and elevated protein levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Patients exhibit accumulation of the branched-chain fatty acid, phytanic acid, in blood and tissues. |
| Reference |
