Human PKC iota / PRKCI Protein (GST Tag)
DXS1179E,nPKC-iota,PKCI
- 100ug (NPP4170) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10534-H09B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | DXS1179E,nPKC-iota,PKCI |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PKCλ/GST chimera consists of 812 amino acids and has a predicted a molecular mass of 93.5 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 100 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 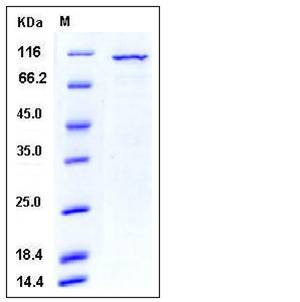 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PKCλ (NP_002731.4) (Met 10-Val 596) was fused with the GST tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Kinase activity untested |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cytoskeletal Proteins |Regulation |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 0.5mM GSH, 0.5mM PMSF, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Protein kinase C iota type, also known as Atypical protein kinase C-lambda/iota, aPKC-lambda/iota and PRKCI, is a cytoplasm, membrane and nucleus protein which belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family and PKC subfamily. PRKCI contains one AGC-kinase C-terminal domain, one OPR domain, one phorbol-ester/DAG-type zinc finger and one protein kinase domain. PRKCI is predominantly expressed in lung and brain, but also expressed at lower levels in many tissues including pancreatic islets. It is highly expressed in non-small cell lung cancers. PRKCI is a calcium-independent, phospholipid-dependent, serine- and threonine-specific kinase. It may play a role in the secretory response to nutrients. PRKCI is involved in cell polarization processes and the formation of epithelial tight junctions. It is implicated in the activation of several signaling pathways including Ras, c-Src and NF-kappa-B pathways. PRKCI functions in both pro- and anti-apoptotic pathways. It functions in the RAC1/ERK signaling required for transformed growth. PRKCI plays a role in microtubule dynamics through interaction with RAB2A and GAPDH and recruitment to vesicular tubular clusters (VTCs). PRKCI might be a target for novel lipid activators that are elevated during nutrient-stimulated insulin secretion. |
| Reference |
