Human PPP3CA / Protein phosphatase 2B Protein (His Tag)
CALN,CALNA,CALNA1,CCN1,CNA1,PPP2B
- 100ug (NPP2426) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13670-H07B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | CALN,CALNA,CALNA1,CCN1,CNA1,PPP2B |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PPP3CA consists of 538 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 60.8 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 60 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 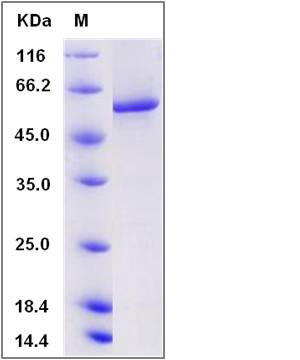 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PPP3CA (Q08209-1) (Ser2-Gln521) was fused with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Using the Octet RED System, the affinity constant (Kd) of human PPPP3CA-His (P13670-H07B) bound to Human PPIA-His (P10436-H08E) was 0.9 nM. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Calcium-binding Proteins and Related Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% glycerol 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | PPP3CA, also known as protein phosphatase 2B, is a member of the PPP phosphatase family, PP-2B subfamily. It is the alpha catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B). PP2B is a holoenzyme that is comprised of a catalytic subunit associated with regulatory subunits. It is a calcium regulated enzyme that is activated by calmodulin and participates in the signaling cascades involved in development of the nervous, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal systems. PPP3CA activates the T cells of the immune system and can be blocked by drugs. It also activates NFATc (a transcription factor) by dephosphorylating it. The activated NFATc is subsequently translocated into the nucleus, where it upregulates the expression of interleukin 2. PPP3CA interacts with CRTC2, MYOZ1, MYOZ2 and MYOZ3. It also interacts with DNM1L. The interaction dephosphorylates DNM1L and regulates its translocation to mitochondria. |
| Reference |
