Human PRKAR1A / PRKAR1 / PKR1 Protein (His Tag)
ACRDYS1,ADOHR,CAR,CNC,CNC1,PKR1,PPNAD1,PRKAR1,TSE1
- 100ug (NPP2430) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14416-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ACRDYS1,ADOHR,CAR,CNC,CNC1,PKR1,PPNAD1,PRKAR1,TSE1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PRKAR1A consists of 391 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 44.3 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 47 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 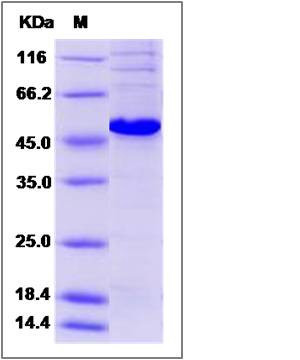 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PRKAR1A (P10644) (Met1-Val381) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Phosphorylation |Serine & threonine kinase |PKA |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM Nacl, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | PRKAR1A, also known as PRKAR1 and PKR1, is one of the regulatory subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA). PKA can be activated by cAMP. cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating PKA, which transduces the signal throughphosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive holoenzyme of PKA is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits of PKA have been identified in humans. PRKAR1A was found to be a tissue-specific extinguisher that down-regulates the expression of seven liver genes in hepatoma x fibroblast hybrids Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been observed. |
| Reference |
