Human PSME3 / PA28-gamma Protein (His Tag)
HEL-S-283,Ki,PA28-gamma,PA28G,PA28gamma,REG-GAMMA
- 100ug (NPP4195) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14682-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | HEL-S-283,Ki,PA28-gamma,PA28G,PA28gamma,REG-GAMMA |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PSME3 consists of 269 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 31.3 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 28-33 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 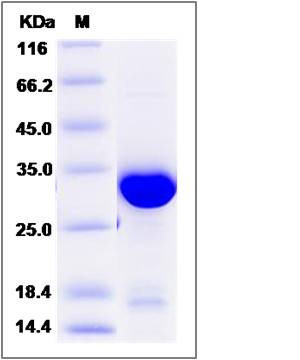 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PSME3 (P61289-1) (Met1-Tyr254) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cell Biology |Cell Cycle |Cell Cycle Inhibitor |p53 pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 200mM NaCl, 40% Glycerol, pH 8.0. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | PSME3, also known as PA28-gamma, is a subunit of proteasome. The 26S proteasome multicatalytic proteinase complex has a highly ordered structure composed of 2 complexes, a 20S core and a 19S regulator. The 20S core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. The 19S regulator is composed of a base, which contains 6 ATPase subunits and 2 non-ATPase subunits, and a lid, which contains up to 10 non-ATPase subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. The immunoproteasome contains an alternate regulator, referred to as the 11S regulator or PA28, that replaces the 19S regulator. Three subunits (alpha, beta and gamma) of the 11S regulator have been identified. PSME3 gene encodes the gamma subunit of the 11S regulator. Six gamma subunits combine to form a homohexameric ring. |
| Reference |
