Human PTH / parathyroid hormone Protein (aa 32-65, GST Tag)
PTH,PTH1
- 100ug (NPP4197) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13192-H09E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | PTH,PTH1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PTH/GST chimera consists of 265 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 31 kDa. It migrates as an approxiamtely 30 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 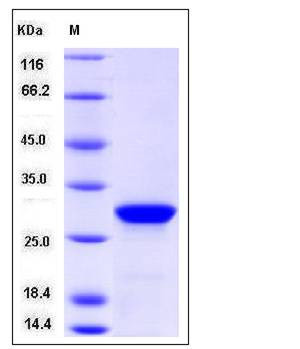 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PTH (P05062) (Ser 32-Phe 65) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurology process |Circadian Rhythm |Hormones |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Parathyroid hormone (PTH), parathormone or parathyrin, is secreted by the chief cells of the parathyroid glands as a polypeptide. PTH elevates calcium level by dissolving the salts in bone and preventing their renal excretion. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) has been proved to play a pivotal role in maintaining myocardial contractility as well as effective natriuresis, and possible pathogenic mechanisms contributing to heart failure secondary to hypocalcemia and hypoparathyroidism. With the increased population of preosteoblastic lineages and the osteoblastic activation, Parathyroid hormone (PTH) drives anabolism in bone. Experiments have recently reported that PTH affects bone cells in a dual pathway - mediating osteoblastic (preosteoblastic) activities or osteocytic synthesis of sclerostin. Defects in PTH are a cause of familial isolated hypoparathyroidism (FIH), also called autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism or autosomal dominant hypocalcemia. FIH is characterized by hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia due to inadequate secretion of parathyroid hormone. Symptoms are seizures, tetany and cramps. |
| Reference |
