Human PTMA Protein (GST Tag)
TMSA
- 100ug (NPP4201) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11407-H09E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | TMSA |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PTMA/GST chimera consists of 341 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 39 kDa. It migrates as an approxiamtely 45 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 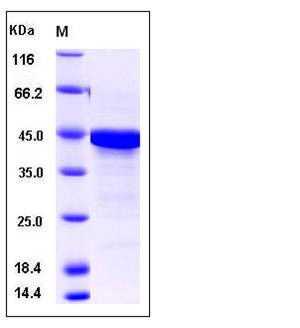 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PTMA (P06454-1) (Ser 2-Asp 111) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Growth Factor & Receptor |Hormones |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | PTMA (prothymosin, alpha, N-GST chimera) is a small, 12.4 kDa protein. It is a 109-111 amino acid long polypeptide as the precursor of thymosin a1. Thymosins are named becaues they were originally isolated from the thymus. But now in many other tissues, thymosins also can be detected. Thymosins have diverse biological activities, and two in particular, thymosins a1 and _4, have potentially important uses in medicine, some of which have already progressed from the laboratory to the clinic. In general, PTMA is associated with cellular proliferation and carcinogenesis (Eschenfeldt et al., 1986), cellular and viral transcription (Cotter et al., 2000), protection against apoptosis and chromatin remodelling (Karetsou et al., 1998). PTMA may have a dual role both intracellulary and extracellulary. In relation to diseases, thymosins have been categorized as biological response modifiers. Thymosin a1 is derived from PTMA. For animals that lack thymus glands, thymosin a1 is responsible for the activity of that preparation in restoring immune function. |
| Reference |
