Human PTPN12 Protein
PTP-PEST,PTPG1
- 100ug (NPP2444) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11556-HNCB |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | PTP-PEST,PTPG1 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human PTPN12 consists of 357 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 41.8 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 41 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gly |
| SDS-PAGE | 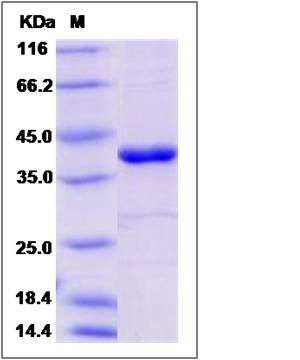 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PTPN12 (AAA36529.1) (Met1-Gln355) was expressed and purified with two additional amino acids (Gly & Pro) at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to dephosphorylate a tyrosine residue in a peptide containing the EGFR Y992 phosphorylation site (Catalog # ES006). The specific activity is >20 µmol/min/mg. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Mitochondrial Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, pH 8.0. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | PTPN12 is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. PTPN12 contains a C-terminal PEST motif, which serves as a protein–protein interaction domain, and may be related to protein intracellular half-life. PTPN12 was found to bind and dephosphorylate the product of oncogene c-ABL, thus may play a role in oncogenesis. PTPN12 was shown to interact with, and dephosphorylate, various of cytoskeleton and cell adhesion molecules, such as p130 (Cas), CAKbeta/PTK2B, PSTPIP1, and paxillin, which suggested its regulatory roles in controlling cell shape and mobilit. |
| Reference |
