Human PTS / PTPS Protein (His Tag)
PTPS,PTS
- 100ug (NPP4205) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14332-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | PTPS,PTS |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PTS consists of 160 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 18.2 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 27 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 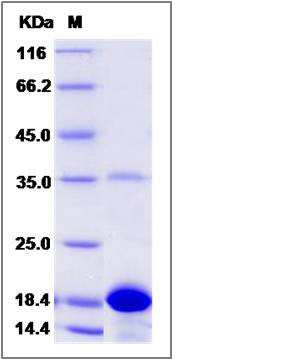 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human PTS (Q03393) (Met1-Glu145) was expressed with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurotransmitter |Biogenic Amines |Dopamine |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 40% Glycerol, pH, 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | PTS(6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase) belongs to the PTPS family. It catalyzes the elimination of inorganic triphosphate from dihydroneopterin triphosphate, which is the second and irreversible step in the biosynthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin from GTP. Tetrahydrobiopterin, also known as BH(4), is an essential cofactor and regulator of various enzyme activities, including enzymes involved in serotonin biosynthesis and NO synthase activity. Mutations in this gene result in hyperphenylalaninemia. PTS is involved in the biosynthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin, an essential cofactor of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases. PTS also catalyzes the transformation of 7,8-dihydroneopterin triphosphate into 6-pyruvoyl tetrahydropterin. Defects in PTS are the cause of BH4-deficient hyperphenylalaninemia type A (HPABH4A), also called 6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin synthase deficiency (PTS deficiency) or hyperphenylalaninemia tetrahydrobiopterin-deficient due to PTS deficiency. HPABH4A is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by depletion of the neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin, and clinically by severe neurological symptoms unresponsive to the classic phenylalanine-low diet. |
| Reference |
