Human Prealbumin / Transthyretin / TTR / PALB Protein (His Tag)
CTS,CTS1,HEL111,HsT2651,PALB,TBPA
- 100ug (NPP4186) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12091-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CTS,CTS1,HEL111,HsT2651,PALB,TBPA |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human TTR comprises 138 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 15.2 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhTTR is approximately 19 and 38 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, corresponding to the monomer and dimer respectively. |
| predicted N | Gly 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 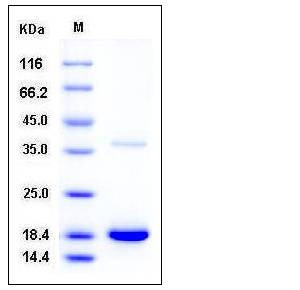 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human TTR (NP_000362.1) (Met 1-Glu 147) with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized recombinant human TTR-His (P12091-H08H)at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind recombinant Canine RBP4-Fc (P70006-D02H) with a linear range of 0.3-10.0 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Acute Phase Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Prealbumin/Transthyretin, also known as ATTR, Prealbumin, TTR and PALB, is a secreted and cytoplasm protein which belongs to the Prealbumin / Transthyretin family. Prealbumin / Transthyretin is detected in serum and cerebrospinal fluid (at protein level). It is highly expressed in choroid plexus epithelial cells. It is also detected in retina pigment epithelium and liver. Each monomer of Prealbumin / Transthyretin has two 4-stranded beta sheets and the shape of a prolate ellipsoid. Antiparallel beta-sheet interactions link monomers into dimers. A short loop from each monomer forms the main dimer-dimer interaction. These two pairs of loops separate the opposed, convex beta-sheets of the dimers to form an internal channel. Prealbumin/Transthyretin is a carrier protein. It transports thyroid hormones in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid, and also transports retinol (vitamin A) in the plasma. Defects in Prealbumin / Transthyretin are the cause of amyloidosis type 1 (AMYL1) which is a hereditary generalized amyloidosis due to Prealbumin / Transthyretin amyloid deposition. Protein fibrils can form in different tissues leading to amyloid polyneuropathies, amyloidotic cardiomyopathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, systemic senile amyloidosis. The diseases caused by mutations include amyloidotic polyneuropathy, euthyroid hyperthyroxinaemia, amyloidotic vitreous opacities, cardiomyopathy, oculoleptomeningeal amyloidosis, meningocerebrovascular amyloidosis, carpal tunnel syndrome, etc. |
| Reference |
