Human Prostasin / Prss8 Protein (His Tag)
CAP1,PROSTASIN
- 100ug (NPP4193) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10287-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CAP1,PROSTASIN |
| Molecular Weight | The mature recombinant human Prss8 consists of 304 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 32.8 kDa. By SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhPrss8 is approximately 40 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ala 30 |
| SDS-PAGE | 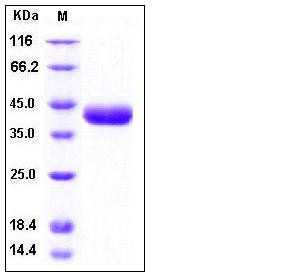 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human Prss8 (NP_002764.1) (Ala 30-Arg 322) was fused with a signal peptide at the N-terminus and a polyhistidine-tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate Boc-QAR-AMC (R&D Systems, Catalog # ES014). The specific activity is >10 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Embryogenesis |Germ Layer Formation |Ectoderm Marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Prostasin (Prss8), also known as channel activating protease 1 (CAP1), is a trypsinlike serine peptidase, and plays important roles in epithelial physiology. It is originally purified as an active, soluble enzyme from human seminal fluid and is highly expressed in prostate, lung, kidney, salivary gland and pancreas. Prostasin is expressed as a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored membrane protein in prostate epithelial cells, and also exists as a secreted proteolytic enzyme possibly via tryptic cleavage of its COOH-terminal hydrophobic domain. Prostasin is found to activate the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) which is tightly regulated and is critical for maintaining salt and fluid balance in the lung and kidney in both normal and pathological conditions. Accordingly, prostasin has been proposed as a target for therapeutic inhibition in cystic fibrosis. In addition, prostasin inhibits prostate and breast cancer cell invasion in vitro, suggesting a functional role as a suppressor of tumor invasion, as well as a regulator of gene expression during inflammation. |
| Reference |
