Human R-Cadherin / CDH4 Protein (His Tag)
CAD4,R-CAD,RCAD
- 100ug (NPP4207) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10230-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CAD4,R-CAD,RCAD |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant pro form of human CAD4 comprises 725 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 80 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rhCAD4 migrates as an approximately 90-100 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 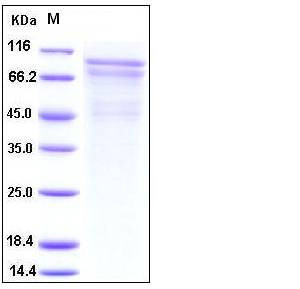 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human CAD4 (NP_001785.2) (Met 1-Ala 734) was expressed with a fused polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of C6 Rat brain glial cells . Immobilized CAD4 (0.8 μg/ml, 100 μl/well) will mediate >20% C6 cell adhesion. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Cadherins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The cadherin superfamily is a large family that engage in both homo- and heterotypic, calcium-dependent, cell-cell adhesion events, and can be divided into at least four subfamilies based on the extracellular (EC) regions and cytoplasmic domains, that is: classical cadherins, desmosomal cadherins, protocadherins, and cadherin-like molecules. Human cadherin 4, type 1, R-cadherin (retinal), also known as CDH4, CAD4 and RCAD, is a classical cadherin from the cadherin superfamily. It is a calcium-dependent adhesion molecule and a type I transmembrane glycoprotein composed of five extracellular cadherin repeats, a transmembrane region and a highly conserved cytoplasmic tail. CDH4 is thought to play an important role during brain segmentation and neuronal outgrowth, and also exerts critical actions in kidney and muscle development. CDH4 is expressed in vascular smooth muscle, pancreatic β-cells, thyroid follicular cells, sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglia, and, possibly, astrocytes and endothelium of the retina. As a classic cadherin, CDH4 forms both homodimers and heterodimers with N-cadherin. The extracellular region of human CDH4 is 96% aa identical to that of mouse CDH4. |
| Reference |
