Human RACK1 / GNB2L1 Protein (His & MBP Tag)
Gnb2-rs1,H12.3,HLC-7,PIG21,RACK1
- 100ug (NPP4209) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12498-H10E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | Gnb2-rs1,H12.3,HLC-7,PIG21,RACK1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human GNB2L1/MBP fusion protein consists of 714 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 78.7 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 70 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 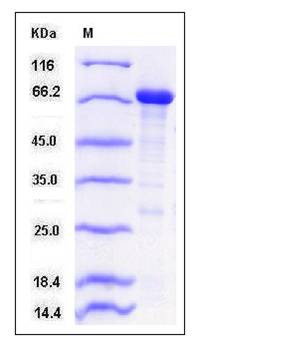 |
| Purity | > 83 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human GNB2L1 (P63244) (Met 1-Arg 317) was fused with an N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged MBP tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |G protein signaling |Heterotrimeric G Protein |G Protein |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | RACK1 (guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 2-like 1), also known as GNB2L1, contains 7 WD repeats and belongs to the WD repeat G protein beta family. In the liver, RACK1 is expressed at higher levels in activated hepatic stellate cells than in hepatocytes or Kupffer cells. It is up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinomas and in the adjacent non-tumor liver tissue. RACK1 is involved in the recruitment, assembly and/or regulation of a variety of signaling molecules. It interacts with a wide variety of proteins and plays a role in many cellular processes. GNB2L1 binds to and stabilizes activated protein kinase C (PKC), increasing PKC-mediated phosphorylation. RACK1 may recruit activated PKC to the ribosome, leading to phosphorylation of EIF6. It inhibits the activity of SRC kinases including SRC, LCK and YES1. RACK1 also inhibits cell growth by prolonging the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. It enhances phosphorylation of BMAL1 by PRKCA and inhibits transcriptional activity of the BMAL1-CLOCK heterodimer. |
| Reference |
