Human REG4 / RELP / GISP Protein (His Tag)
GISP,REG-IV,RELP
- 100ug (NPP2459) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11186-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | GISP,REG-IV,RELP |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human REG4 consists of 147 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 17.4 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh REG4 is approximately 18 and 22 kDa due to different glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ala 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 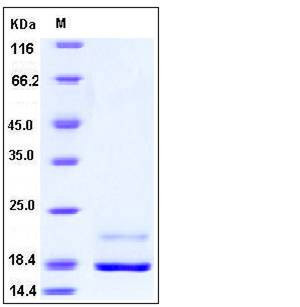 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human REG4 (NP_001152824.1) (Met 1-Pro 158) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the proliferation of HCT-116 human colorectal carcinoma cells (ATCC: CCL-247) under low serum conditions. The ED50 for this effect is typically 4-20 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Lectin |C-tyep lectin | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Regenerating islet-derived protein 4, also known as REG-like protein, REG4, GISP and RELP, a member of the regenerating gene family belonging to the calcium (C-type) dependent lectin superfamily, has been found to be involved in malignancy in several different organs including the stomach, colorectum, pancreas and prostate. It is highly expressed in the gastrointestinal tract and markedly up-regulated in colon adenocarcinoma, pancreatic cancer, gastric adenocarcinoma, and inflammatory bowel disease. Expression of the Reg4 in different cell types has been associated with regeneration, cell growth and cell survival, cell adhesion and resistance to apoptosis. REG4 protein overexpression is associated with an unfavorable response to preoperative chemoradiotherapy and may be used as a predictive biomarker clinically. REG4 may play an important role in the development and progression of colorectal cancer, as well as in intestinal morphogenesis and epithelium restitution. |
| Reference |
