Human RELT / TNFRSF19L Protein (His Tag)
TNFRSF19L,TRLT
- 100ug (NPP4216) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10530-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | TNFRSF19L,TRLT |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human RELT consists of 146 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 15.7 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhRELT is approximately 25-30 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ser 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 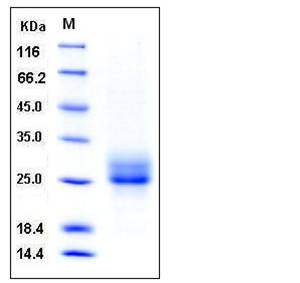 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human RELT (NP_116260.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Ala 160) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus, with 127R/G & 129R/G mutations. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Regulation of Apoptosis by TNF Superfamily Members |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Receptor expressed in lymphoid tissues (RELT), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 19-like (TNFRSF19L), is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor is especially abundant in hematologic tissues. It has been shown to activate the NF-kappaB pathway and selectively bind TNF receptor-associated factor 1. RELT/TNFRSF19L is capable of stimulating T-cell proliferation in the presence of CD3 signaling, which suggests its regulatory role in immune response. RELT/TNFRSF19L is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with a cysteine-rich extracellular domain, possessing significant homology to other members of the TNFR superfamily, especially TNFRSF19, DR3, OX40, and LTbeta receptor. RELT/TNFRSF19L is able to activate the NF-kappaB pathway and selectively binds tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1. RELT/TNFRSF19L is able to activate the NF-κB pathway and selectively binds tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1. Although the soluble form of RELT fusion protein does not inhibit the one-way mixed lymphocyte reaction, immobilized RELT/TNFRSF19L is capable of costimulating T-cell proliferation in the presence of CD3 signaling. |
| Reference |
