Human ROBO2 Protein (His Tag)
KIAA1568,ROBO2,SAX3
- 100ug (NPP2469) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10310-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | KIAA1568,ROBO2,SAX3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ROBO2 consists of 849 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 94.2 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 116 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ser 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 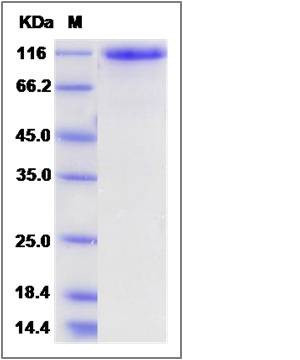 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ROBO2 (Q9HCK4-1) (Met1-Pro859) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Cell Type Marker in Neurodevelopment |Neuronal Cell Markers |Axon marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ROBO2 belongs to the ROBO family. Members of the ROBO family are a group of highly conserved transmembrane glycoproteins that make up a small subgroup of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. They are best known for their roles as receptors for the Slit family of repellent axon guidance cues. In structure, ROBOs are characterized by five C2-type Ig-like repeats, three fibronectin type III domains, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular domain with three (ROBO3) or four (ROBO1, 2) CC (conserved cytoplasmic) motifs. ROBO2 is a receptor for SLIT2, and probably SLIT1, which are thought to act as molecular guidance cue in cellular migration, including axonal navigation at the ventral midline of the neural tube and projection of axons to different regions during neuronal development. ROBO2 also abrogates SLIT-ROBO signaling in vitro. |
| Reference |
