Human S100A14 / S114 Protein (His Tag)
BCMP84,S100A15
- 100ug (NPP4230) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12251-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | BCMP84,S100A15 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human S100A14 consisting of 114 amino acids and migrates as an 13 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 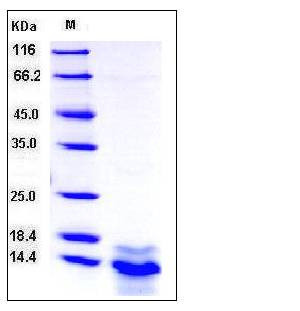 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the native human S100A14 (NP_065723.1) (Gly 2-His 104) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurotransmission |Calcium Signaling |Calcium Binding Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 20% glycerol, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | S100 protein is a family of low molecular weight protein found in vertebrates characterized by two EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. There are at least 21 different S100 proteins, and the name is derived from the fact that the protein is 100% soluble in ammonium sulfate at neutral pH. Most S100 proteins are disulfide-linked homodimer, and is normally present in cells derived from the neural crest, chondrocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, etc. S100 proteins have been implicated in a variety of intracellular and extracellular functions. They are involved in regulation of protein phosphorylation, transcription factors, the dynamics of cytoskeleton constituents, enzyme activities, cell growth and differentiation, and the inflammatory response. Protein S100-A14, also known as S100 calcium-binding protein A14, S114 and S100A14, is a cytoplasm protein which belongs to the S-100 family. It is expressed at highest levels in colon and at moderate levels in thymus, kidney, liver, small intestine, and lung. Low expression in heart and no expression is seen in brain, skeletal muscle, spleen, placenta and peripheral blood leukocytes. |
| Reference |
