Human S100A3 / S100E Protein (His & MBP Tag)
S100E
- 100ug (NPP4232) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11136-H10E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | S100E |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human S100A3/MBP fusion protein consists of 498 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 55.3 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 50 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 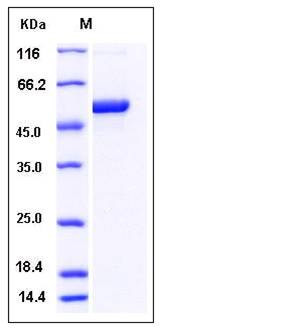 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human S100A3 (P33764) (Met 1-Gln 101) was fused with an N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged MBP tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Signaling Pathway |Calcium Signaling |Calcium Binding Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 20% glycerol, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Protein S100-A3, also known as Protein S-100E, S100 calcium-binding protein A3, S100A3 and S100E, is a member of the S-100 family. S100A3 / S100E contains 2 EF-hand domains. S100A3 / S100E is highly expressed in the differentiating cuticular cells within the hair follicle and organized into mature hair cuticles. High concentrations of S100A3 homotetramer might provide the millimolar level of Ca2+ required for hair cuticular barrier formation. S100A3 / S100E is a unique member of the Ca2+-binding S100 protein family with the highest cysteine content and affinity for Zn2+. S100A3 / S100E binds both calcium and zinc. S100A3 / S100E probably binds 2 zinc ions per molecule. It may be involved in calcium-dependent cuticle cell differentiation and hair shaft formation. S100A3 plays an important role in calcium-dependent processes leading to hair shaft formation. S100A3 / S100E is a unique protein among all members of the calcium-binding S100 family, is specifically expressed at the inner endocuticle of human hair fibers. Upon hair damage, S100A3 / S100E is released from hair fibers and possibly destabilizes the hair tissue architecture. |
| Reference |
