Human SCARB1 / CD36L1 / CLA-1 Protein (His & Fc Tag)
CD36L1,CLA-1,CLA1,HDLQTL6,SR-BI,SRB1
- 100ug (NPP4243) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11069-H03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD36L1,CLA-1,CLA1,HDLQTL6,SR-BI,SRB1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SCARB1/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer consists of 659 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 78 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhSCARB1/Fc monomer is approximately 110-115 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Pro 33 |
| SDS-PAGE | 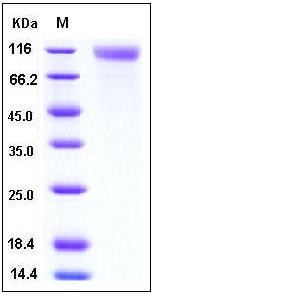 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SCARB1 (NP_005496.4) extracellular domain (Pro 33-Tyr 443) was fused with the C-terminal polyhistidine-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to bind recombinant mouse ApoAI in a functional ELISA. 2. Measured by its ability to bind recombinant Human ApoAI in a functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolic signaling pathways |Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism |Cholesterol Metabolism | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Scavenger receptor class B, member 1 (SCARB1), also known as CD36L1, is a member of the scavenger receptor family. SCARB1 is expressed primarily in liver and non placental steroidogenic tissues, and predominantly localized to cholesterol and sphingomyelin-enriched domains within the plasma membrane. SCARB1 is proposed as a receptor for different ligands such as phospholipids, cholesterol ester, lipoproteins, phosphatidylserine and apoptotic cells, and is involved in a wide variety of physilogical processes. As a key component in the reverse cholesterol transport pathway, SCARB1 binds high density lipoproteins (HDLs) and mediates selective cholesterol uptake by a mechanism distinct from the LDL pathway. High density lipoproteins (HDLs) play a critical role in cholesterol metabolism and their plasma concentrations are inversely correlated with risk for atherosclerosis. SCARB1 may thus serve as a useful marker that predicts variation in baseline lipid levels and postprandial lipid response. The mouse SCARB1 has been shown to exert actions in determining the levels of plasma lipoprotein cholesterol and the accumulation of cholesterol stores in the adrenal gland. |
| Reference |
