Human SCG2 / Secretogranin II Protein (His Tag)
CHGC,EM66,SgII,SN
- 100ug (NPP4245) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13441-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CHGC,EM66,SgII,SN |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SCG2 comprises 612 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 70.5 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 71 and 65 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Pro 17 |
| SDS-PAGE | 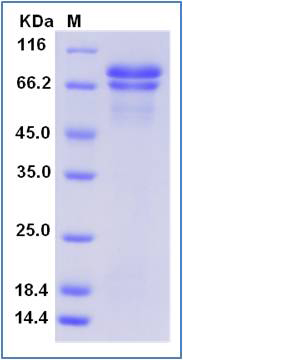 |
| Purity | (58.1+30.8) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SCG2 (AAH22509.1) (Met1-Met617) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Reproduction |Hormones |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Kit ligand, also known as Hematopoietic growth factor KL, Mast cell growth factor, Steel factor, Stem cell factor, c-Kit ligand, Kitlg and KITL, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the SCF family. KITL / kit ligand also belongs to the family of dimeric transmembrane growth factors. The soluble form of KIT ligand is a secreted protein. Mast cells are thought to participate in a variety of immune responses, such as parasite resistance and the allergic reaction. Mast cell development depends on stem cell factor (Kit ligand) and its receptor, c-Kit. KITL / kit ligand stimulates the proliferation of mast cells. KITL / kit ligand is able to augment the proliferation of both myeloid and lymphoid hematopoietic progenitors in bone marrow culture. Efficient cell surface presentation of KITL / kit ligand is essential for the migration, proliferation, and survival of melanocytes, germ cells, hemopoietic stem cells, and mastocytes. KITL / kit ligand acts synergistically with other cytokines, probably interleukins. KITL / kit ligand plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of the melanocyte lineage in adult skin. It exerts permanent survival, proliferation and migration functions in Kit receptor-expressing melanocytes. KITL / kit ligand misexpression in some hyperpigmented lesions may open the avenue for Kitl-dependent treatment of pathological skin conditions. |
| Reference |
