Human SECTM1 / K12 Protein (His Tag)
K12
- 100ug (NPP4250) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12269-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | K12 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SECTM1 consists of 128 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 14 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhSECTM1 is approximately 23 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions |
| predicted N | Gln 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 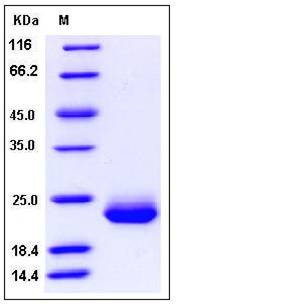 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SECTM1 (Q8WVN6-1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Gly 145) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Intracellular Kinases |NFkB Pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Secreted and transmembrane 1 (SECTM1), also known as K12, is a transmembrane and secreted protein with characteristics of a type 1a transmembrane protein of SECTM family. It is found in a perinuclear Golgi-like pattern and thought to be involved in hematopoietic and/or immune system processes. The human K12 protein has been shown to be primarily expressed in spleen, prostate, testis, small intestine, and in peripheral blood leukocytes. The K12 protein is expressed on the cell surface in such small amounts as to preclude detection. Alternatively, it may be that K12 on the cell surface is rapidly cleaved to generate a soluble K12 protein. Immunohistochemical analysis of peripheral blood cells shows that K12 is found in leukocytes of the myeloid lineage, with the strongest staining observed in granulocytes and no detectable expression in lymphocytes. May be involved in thymocyte signaling. It had been suggested a role for thymic microenvironment-produced K12 in regulation of thymocyte signaling and cytokine release, particularly in the setting of thymus pathology where IFN-gamma is upregulated such as myasthenia gravis. In addition, as a putative natural CD7 ligand, SECTM1/K12 may be responsible for the costimulatory role it plays in T cell activation. |
| Reference |
