Human SELM / Selenoprotein M Protein (His Tag)
SEPM
- 100ug (NPP4251) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13508-H08E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | SEPM |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SELM comprises 133 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 15.4KDa. It migrates as an approximately 19 kDa band d in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 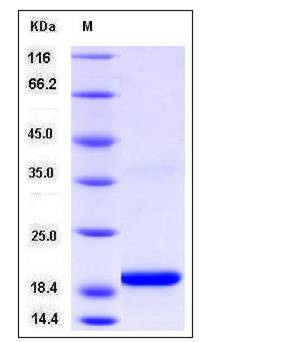 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human SELM (Q8WWX9) (Ala 24-Leu 145) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus and an initial Met at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolic signaling pathways |Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 50mM NaCl, 50mM Arg, 0.3% Tween 20, 5% glycerol, pH 8.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Selenoprotein M is a selenoprotein, which contains a selenocysteine (Sec) residue at its active site. The selenocysteine M is encoded by the UGA codon that normally signals translation termination. The 3' UTR of selenoprotein genes have a common stem-loop structure, the sec insertion sequence (SECIS), that is necessary for the recognition of UGA as a Sec codon rather than as a stop signal. This gene is expressed in a variety of tissues, and the protein is localized to the perinuclear structures. Selenoprotein M May function as a thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase that participates in disulfide bond formation. This protein is widely expressed and is highly expressed in brain. It is found in Cytoplasm, perinuclear region, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus. Localized to perinuclear structures corresponding to Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum. Experiments results have suggested that selenoprotein M may have an important role in protecting against oxidative damage in the brain and may potentially function in calcium regulation. |
| Reference |
