Human SIGLEC5 Protein
CD170,CD33L2,OB-BP2,OBBP,OBBP2,SIGLEC-5,SIGLEC5
- 100ug (NPP2499) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11798-HCCH |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD170,CD33L2,OB-BP2,OBBP,OBBP2,SIGLEC-5,SIGLEC5 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SIGLEC5 consists of 425 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 47.2 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 67 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 17 |
| SDS-PAGE | 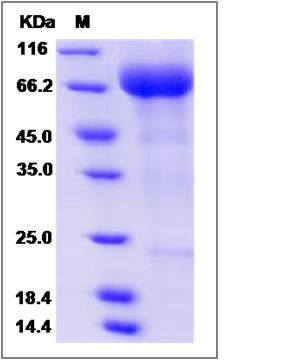 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SIGLEC5 (O15389) (Met1-Thr 434) was expressed with six amino acids (LEVLFQ) at the C-terminus was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | SIGLEC5 contains 2 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and 1 Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain. It belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and SIGLEC (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin) family. SIGLEC5 is expressed by monocytic/myeloid lineage cells. It is found at high levels in peripheral blood leukocytes, spleen, bone marrow and at lower levels in lymph node, lung, appendix, placenta, pancreas and thymus. It is also expressed by monocytes and neutrophils but absent from leukemic cell lines representing early stages of myelomonocytic differentiation. SIGLEC5 is a putative adhesion molecule that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells. It binds equally to alpha-2,3-linked and alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid. The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. |
| Reference |
