Human SIRPG Protein (Fc Tag)
bA77C3.1,CD172g,SIRP-B2,SIRPB2,SIRPgamma
- 100ug (NPP3957) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P16111-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | bA77C3.1,CD172g,SIRP-B2,SIRPB2,SIRPgamma |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SIRPG consists of 577 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 64.1 kDa. |
| predicted N | Glu 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 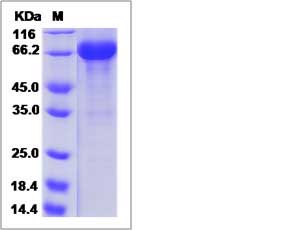 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SIRPG (NP_061026.2) (Met1-Ser364) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Signal-regulatory protein gamma (SIRPG/SIRP gamma) also known as CD172 antigen-like family member B, CD172g, and CD172g antigen, is a member of the signal-regulatory protein (SIRP) family, and also belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. SIRP family members are receptor-type transmembrane glycoproteins known to be involved in the negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled signaling processes. SIRPG/SIRP gamma/CD172g is probable immunoglobulin-like cell surface receptor. On binding with CD47, SIRPG can mediate cell-cell adhesion. SIRPG/SIRP gamma is engagement on T-cells by CD47 on antigen-presenting cells results in enhanced antigen-specific T-cell proliferation and costimulates T-cell activation. SIRPG/SIRP gamma/CD172g is detected in liver, and at very low levels in brain, heart, lung, pancreas, kidney, placenta and skeletal muscle. Expressed on CD4+ T-cells, CD8+ T-cells, CD56-bright natural killer (NK) cells, CD20+ cells, and all activated NK cells. This cytokine is mainly present in the paracortical T-cell area of lymph nodes, with only sparse positive cells in the mantle and in the germinal center of B-cell follicles. In the thymus, SIRPG is primarily expressed in the medulla on mature T-lymphocytes that have undergone thymic selection. |
| Reference |
