Human SLAMF6 / Ly108 Protein (His Tag)
CD352,KALI,KALIb,Ly108,NTB-A,NTBA,SF2000
- 100ug (NPP2325) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11945-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD352,KALI,KALIb,Ly108,NTB-A,NTBA,SF2000 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SLAMF6 consists of 216 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 24.3 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhSLAMF6 is approximately 38-40 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 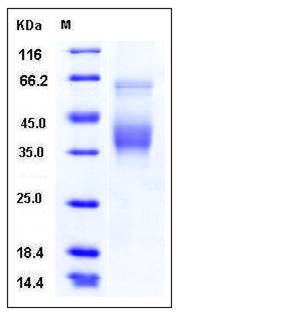 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SLAMF6 (Q96DU3-1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Met 226) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to bind biotinylated recombinant human SH2D1A in a functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | SLAM family member 6, also known as Activating NK receptor, NK-T-B-antigen, NTB-A, SLAMF6, KALI and Ly108, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the CD2 subfamily of the immunoglobulin superfamily. SLAMF6 / Ly108 contains one Ig-like (immunoglobulin-like) domain. It is expressed by all (resting and activated) natural killer cells (NK), T- and B-lymphocytes. SLAMF6 / Ly108 triggers cytolytic activity only in natural killer cells (NK) expressing high surface densities of natural cytotoxicity receptors. SLAMF6 / Ly108 is a homodimer. It interacts with PTN6 and, upon phosphorylation, with PTN11 and SH2D1A/SAP. SLAMF6 / Ly108 undergoes tyrosine phosphorylation and associates with the Src homology 2 domain-containing protein (SH2D1A) as well as with SH2 domain-containing phosphatases (SHPs). It may function as a coreceptor in the process of NK cell activation. SLAMF6 / Ly108 can also mediate inhibitory signals in NK cells from X-linked lymphoproliferative patients. |
| Reference |
