Human SMPD1 / ASM Protein (His Tag)
ASM,ASMASE,NPD
- 100ug (NPP4278) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11087-H07B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | ASM,ASMASE,NPD |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human SMPD1 consists of 563 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 65 kDa as estimated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 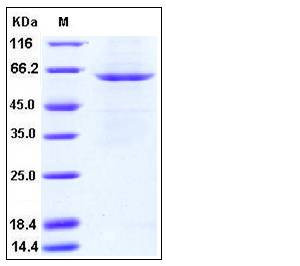 |
| Purity | > 91 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human SMPD1 isoform 1 (NP_000534.3) (Gly 85-Cys 631) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave 2-N-Hexadecanoylamino-4-nitrophenylphosphorylcholine (HNPPC) . The specific activity is 77 pmol/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Metabolism |Lipid metabolism |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% glycerol 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1 (SMPD1) , also known as ASM ( acid sphingomyelinase ), is a member of the acid sphingomyelinase family of enzymes. Three isoforms have been identified, isoform 1 is 631 amino acids (aa) in length as the pro form, while Isoform 2 and isoform 3 have lost catalytic activity. The active SMPD1 isoform 1 contains one saposin B-type domain that likely interacts with sphingomyelin, and a catalytic region. Human SMPD1 is 86% aa identical to mouse SMPD1. SMPD1 is a monomeric lysosomal enzyme that converts sphingomyelin (a plasma membrane lipid ) into ceramide through the removal of phosphorylcholine. This generates second messenger components that participate in signal transduction. Defects in SMPD1 are the cause of Niemann-Pick disease type A (NPA) and type B (NPB), also known as Niemann-Pick disease classical infantile form and Niemann-Pick disease visceral form. Niemann-Pick disease is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous recessive disorder. NPB has little if any neurologic involvement and patients may survive into adulthood. |
| Reference |
