Human SNCA / alpha-Synuclein Protein
NACP,PARK1,PARK4,PD1
- 100ug (NPP4283) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12093-HNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | NACP,PARK1,PARK4,PD1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SNCA consisting of 140 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 14.5 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 19 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 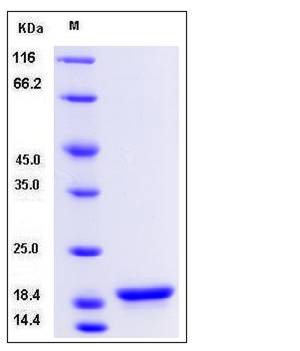 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human SNCA isoform 1 (P37840-1) (Met 1-Ala 140) was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Cell Type Marker in Neurodevelopment |Neuronal Cell Markers |Synapse & Synaptic Proteins |Postsynaptic Density Protein |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Alpha-Synuclein (alpha-Syn), also known as NACP or SNCA, exists as at least two structural isoforms: one is helix-rich, membrane-bound form that both the N- and C-terminal regions of alpha-synuclein are tightly associated with membranes and the other is disordered, cytosolic form. Synuclein is found predominantly in the presynaptic termini, in both free or membrane-bound forms. SNCA is extensively localized in nucleus of neurons. It has been shown that alpha-Synuclein was highly expressed in the mitochondria in olfactory bulb, hippocampus, striatum, and thalamus, where the cytosolic alpha-Synuclein was also rich. Normally the unstructured soluble type of alpha-synuclein can aggregate to form insoluble fibrils in pathological conditions characterized by Lewy bodies, such as Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and multiple system atrophy. SNCA abnormality and mitochondrial deficiency are two major changes in the brain of patients with Parkinson's disease (PD). In addition, alpha-synuclein is an abundant component of Lewy bodies in sporadic Parkinson's disease and diffuse Lewy body disease. |
| Reference |
