Human SPINK4 Protein (His Tag)
HEL136,MGC133107,PEC-60,PEC60,SPINK4
- 100ug (NPP4288) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11669-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | HEL136,MGC133107,PEC-60,PEC60,SPINK4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SPINK4 consists of 71 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 8 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 10 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 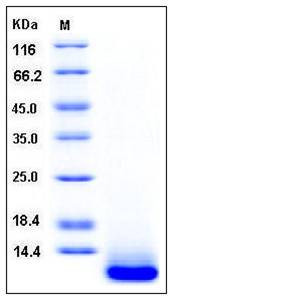 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SPINK4 (NP_055286.1) (Met 1-Cys 86) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Embryogenesis |Germ Layer Formation |Ectoderm |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 4, also known as Peptide PEC-60 homolog and SPINK4, is a secreted protein which contains one Kazal-like domain. SPINK4 is a member of the SPINK protein family. The gene family of serine protease inhibitors of the Kazal type (SPINK) are functional and positional candidate genes for celiac disease (CD). SPINK1 plays an important role in protecting the pancreas against excessive trypsinogen activation. It is a potent natural inhibitor of pancreatic trypsin activity. SPINK1 mutations are associated with the development of acute and chronic pancreatitis and have been detected in all forms of chronic pancreatitis. SPINK2 functions as a trypsin/acrosin inhibitor and is synthesized mainly in the testis and seminal vesicle where its activity is engaged in fertility. The SPINK2 protein contains a typical Kazal domain composed by six cysteine residues forming three disulfide bridges. SPINK9 was identified in human skin. Its expression was strong in palmar epidermis, but not detectable or very low in non palmoplantar skin. |
| Reference |
