Human STK40 Protein (His & GST Tag)
SgK495,SHIK
- 100ug (NPP2521) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11597-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | SgK495,SHIK |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human STK40 /GST chimera consists of 672 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 76.8 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 85 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 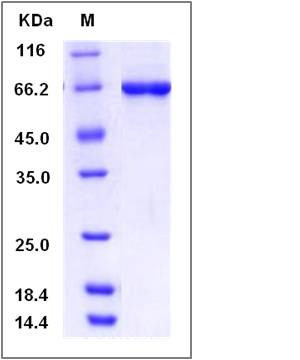 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human STK40 (NP_114406) (Met1-Lys435) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Kinase activity untested |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Kinase |Intracellular Kinase |Other Intracellular Protein Kinases |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 3mM DTT, 0.5M Urea, 0.5mM GSH, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | STK40 localized to both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. It is ubiquitously expressed. Mechanistically, Stk40 interacts with Rcn2, which also activates Erk1/2 to induce ExEn specification in mouse ESCs. Stk40 is able to activate the Erk/MAPK pathway and induce extraembryonic-endoderm (ExEn) differentiation in mouse ESCs. Interestingly, cells overexpressing Stk40 exclusively contribute to the ExEn layer of chimeric embryos when injected into host blastocysts. In contrast, deletion of Stk40 in ESCs markedly reduces ExEn differentiation in vitro. STK40 has a central serine/threonine protein kinase domain and is homologous to TRB-3, a protein that regulates activation of MAP kinases and inhibits NFκB-mediated gene transcription. Similarly, overexpression of STK40 inhibits NFκB activation triggered by TNF and also inhibits p53-mediated transcription. There are four named isoforms of STK40 that are produced as a result of alternative splicing. |
| Reference |
