Human STXBP1 / UNC18A Protein (His & GST Tag)
MUNC18-1,NSEC1,P67,RBSEC1,UNC18
- 100ug (NPP4294) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11751-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | MUNC18-1,NSEC1,P67,RBSEC1,UNC18 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human STXBP1/GST chimera consists of 831 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 95.4 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 80 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 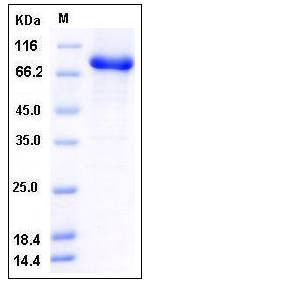 |
| Purity | > 93 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human STXBP1 isoform 1 (P61764-1) (Met 1-Ser 594) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Cancer |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 0.5mM PMSF, 10% gly, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Syntaxin-binding protein 1, also known as N-Sec1, Protein unc-18 homolog 1, MUNC18-1 and STXBP1, is a peripheral membrane protein which belongs to the STXBP / unc-18 / SEC1 family. STXBP1 is an evolutionally conserved neuronal Sec1/Munc-18 (SM) protein that is essential in synaptic vesicle release in several species. It may participate in the regulation of synaptic vesicle docking and fusion, possibly through interaction with GTP-binding proteins. STXBP1 is essential for neurotransmission and binds syntaxin, a component of the synaptic vesicle fusion machinery probably in a 1:1 ratio. It can interact with syntaxins 1, 2, and 3 but not syntaxin 4. STXBP1 may also play a role in determining the specificity of intracellular fusion reactions. Defects in STXBP1 are the cause of epileptic encephalopathy early infantile type 4 (EIEE4). Affected individuals have neonatal or infantile onset of seizures, suppression-burst pattern on EEG, profound mental retardation, and MRI evidence of hypomyelination. |
| Reference |
