Human SULT1B1 / ST1B2 Protein (His Tag)
ST1B1,ST1B2,SULT1B2
- 100ug (NPP4296) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11592-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | ST1B1,ST1B2,SULT1B2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SULT1B1 comprises 302 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 35.7 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 34 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 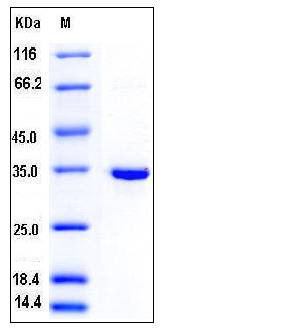 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SULT1B1 (NP_055280.2) (Leu 2-Ile 296) was expressed, with a N-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to transfer sulfate from PAPS to 1-Napthol. The specific activity is > 40 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Hormones |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 0.1 M NaCl, 10% glycerol, 1mM DTT, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Sulfotransferase family cytosolic 1B member 1, also known as Sulfotransferase 1B1, Sulfotransferase 1B2, Thyroid hormone sulfotransferase, SULT1B1 and ST1B2, is a cytoplasm protein which belongs to the sulfotransferase 1 family. Sulfotransferase enzymes catalyze the sulfate conjugation of many hormones, neurotransmitters, drugs, and xenobiotic compounds. These cytosolic enzymes are different in their tissue distributions and substrate specificities. SULT1B1 is highly expressed in the liver, peripheral blood leukocytes, colon (mucosal lining), small intestine (jejunum) and spleen. A lesser expression of SULT1B1 was observed in the lung, placenta and thymus. SULT1B1 catalyzes the sulfate conjugation of many hormones, neurotransmitters, drugs and xenobiotic compounds. Sulfonation increases the water solubility of most compounds, and therefore their renal excretion, but it can also result in bioactivation to form active metabolites. SULT1B1 sulfates dopamine, small phenols such as 1-naphthol and p-nitrophenol and thyroid hormones, including 3,3'-diiodothyronine, triidothyronine, reverse triiodothyronine and thyroxine. |
| Reference |
