Human SUSD4 / Sushi domain-containing Protein 4 Protein (Fc Tag)
PRO222
- 100ug (NPP2528) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13488-H05H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | PRO222 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SUSD4/mFc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 483 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 53.8 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 67 in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Phe 42 |
| SDS-PAGE | 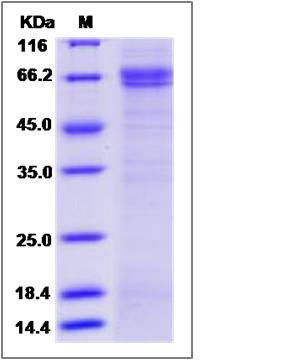 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SUSD4 (Q5VX71-3) (Met1-Phe290) was fused with Fc region of mouse IgG at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | SUSD4, also known as sushi domain-containing protein 4, is a hypothetical cell surface protein whose tissue distribution and function are completely unknown. SUSD4 is detectable in murine brains, eyes, spinal cords, and testis but not other tissues. In brains, SUSD4 is highly expressed in the white matter on oligodendrocytes/axons, and in eyes, it is exclusively expressed on the photoreceptor outer segments. In in vitro complement assays, SUSD4 augments the alternative but not the classical pathway of complement activation at the C3 convertase step. SUSD4 deficiency may cause autism or Fryns syndrome, both of which are genetic diseases with severe abnormal neurological development and/or functions. |
| Reference |
