Human Semaphorin 5A / SEMA5A Protein (His Tag)
SEMAF,semF
- 100ug (NPP4252) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11300-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | SEMAF,semF |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SEMA5A consists of 957 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 107 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh SEMA5A is approximately 130-140 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 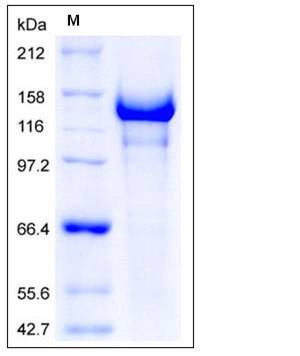 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SEMA5A (NP_003957.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Met 968) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurology process |Growth and Development |Axon Guidance |Semaphorin, Plexin, & Neuropilin |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Semaphorins are secreted, transmembrane, and GPI-linked proteins, defined by cysteine-rich semaphorin protein domains, that have important roles in a variety of tissues. Humans have 20 semaphorins, Drosophila has five, and two are known from DNA viruses. Semaphorins are found in nematodes and crustaceans but not in non-animals. They are grouped into eight classes on the basis of phylogenetic tree analyses and the presence of additional protein motifs. Semaphorins have been implicated in diverse developmental processes such as axon guidance during nervous system development and regulation of cell migration. Semaphorin-5A, also known as Semaphorin-F, Sema F, SEMA5A and SEMAF, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the semaphorin family. Semaphorin5A / SEMA5A contains one PSI domain, one Sema domain and seven TSP type-1 domains. It may act as positive axonal guidance cues. Semaphorin5A / SEMA5A is an axon regulator molecule and plays major roles during neuronal and vascular development. It plays an essential role in embryonic development. Semaphorin5A / SEMA5A induces endothelial cell migration from pre-existing vessels. It also plays a role in autism, reducing the ability of neurons to form connections with other neurons in certain brain regions. |
| Reference |
