Human SerpinA3 / AACT Protein (His Tag)
AACT,ACT,GIG24,GIG25,MGC88254,SERPINA3
- 100ug (NPP4254) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10307-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AACT,ACT,GIG24,GIG25,MGC88254,SERPINA3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human SERPINA3 consisting of 409 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 46.5 kDa. As a result of different glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 45 kDa and 55-70 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Asn 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 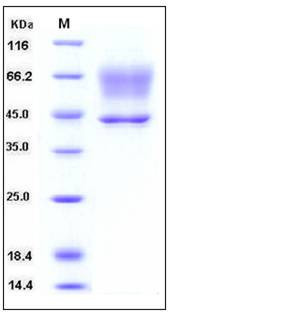 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human SERPINA3 (NP_001076.2) (Met 1-Ala 423) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit trypsin cleavage of a fluorogenic peptide substrate, Mca-RPKPVE-Nval-WRK(Dnp)-NH2 (Anaspec, Catalog# 27114). The IC50 value is < 5 nM. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Acute Phase Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 25mM HEPES, 0.15M NaCl, pH 7.8 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Human SerpinA3, also known as Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin (AACT), is a plasma alpha globulin glycoprotein, and is a member of serpin superfamily of the serine protease inhibitors consisting of at least 35 members. SerpinA3 has been demonstrated to inhibit the activity of certain serine proteases, such as cathepsin G found in neutrophils, and chymases present in mast cells, by inducing a major conformational rearrangement, and thus protects some tissues from damage caused by proteolytic enzymes. This enzyme is produced primarily in the liver, and is identified as an acute-phase inflammatory protein. SerpinA3 deficiency has been associated with liver disease, and mutations of this gene have been observed in patients with Parkinson disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In addition, ACT gene polymorphism has been implicated with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), as well as stroke, since SerpinA3 is a major constituent of the plaques in AD and an inhibitor of amyloid beta peptide degradation. |
| Reference |
