Human TH / Tyrosine Hydroxylase Protein (His Tag)
DYT14,DYT5b,TYH
- 100ug (NPP4308) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10684-H07B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | DYT14,DYT5b,TYH |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human TH consists of 515 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 57.6 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 75 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 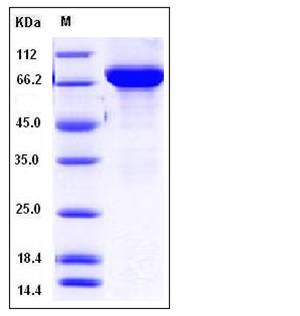 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human TH isoform 2 (P07101-3) (Pro 2-Gly 497) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Apoptosis |Oxidative Stress |Pro-oxidant Molecules | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) is a rate-limiting enzyme in catecholamine synthesis. Tyrosine hydroxylase activity is modulated by protein-protein interactions with enzymes in the same pathway or the tetrahydrobiopterin pathway, structural proteins considered to be chaperones that mediate the neuron's oxidative state. It is phosphorylated at serine (Ser) residues Ser8, Ser19, Ser31 and Ser40 in vitro. The phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase at Ser19 or Ser8 has no direct effect on tyrosine hydroxylase activity. As tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) catalyses the formation of L-DOPA, the rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of DA, the Parkinson's disease (PD) can be considered as a TH-deficiency syndrome of the striatum. A direct pathogenetic role of TH has also been suggested, as the enzyme is a source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in vitro and a target for radical-mediated oxidative injury. Recently, it has been demonstrated that L-DOPA is effectively oxidized by mammalian Tyrosine hydroxylase in vitro, possibly contributing to the cytotoxic effects of DOPA. |
| Reference |
