Human TLK2 / PKU-ALPHA Protein (aa 397-772)
HsHPK,PKU-ALPHA
- 100ug (NPP4318) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11551-HNCB |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | HsHPK,PKU-ALPHA |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human TLK2 consists of 378 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 43.6 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 44 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly |
| SDS-PAGE | 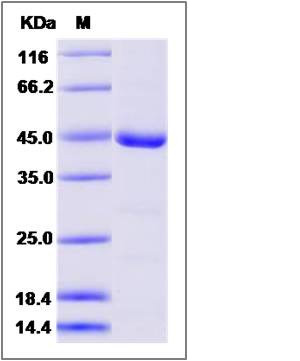 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human TLK2 (Q86UE8-1) (Leu397-Asn772) was fused with two additional amino acids (Gly & Pro) at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Kinase activity untested |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Kinase |Intracellular Kinase |Other Intracellular Protein Kinases |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 3mM DTT, 10% glycerol, pH 8.0. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Serine / threonine-protein kinase tousled-like 2, also known as PKU-alpha, Tousled-like kinase 2 and TLK2, is a nucleus protein which belongs to the protein kinase superfamily and Ser/Thr protein kinase family. The tousled-like kinases are an evolutionarily conserved family of proteins implicated in DNA repair, DNA replication and mitosis in metazoans and plants. Their absence from the yeasts and other eukaryotic 'microbes' suggests a specific role for them in the development of multicellular organisms. Tousled-like kinase 2 / TLK2 is widely expressed. It is present in fetal placenta, liver, kidney, pancreas, heart and skeletal muscle. It is also found in adult cell lines. Tousled-like kinase 2 / TLK2 contains one protein kinase domain. Tousled-like kinase 2 / TLK2 is rapidly and transiently inhibited by phosphorylation following the generation of DNA double-stranded breaks during S-phase. This is cell cycle checkpoint and ATM-pathway dependent and appears to regulate processes involved in chromatin assembly. |
| Reference |
