Human TLR4 / CD284 Protein (His Tag)
ARMD10,CD284,TLR-4,TLR4,TOLL
- 100ug (NPP4320) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10146-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | ARMD10,CD284,TLR-4,TLR4,TOLL |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human TLR4 consists of 619 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 70.5 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 68 Kda in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 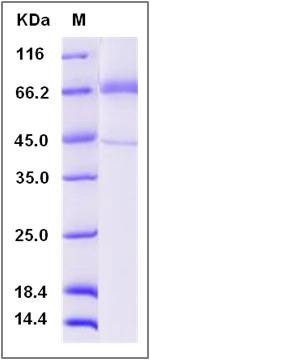 |
| Purity | > 87 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human TLR4 (Met 1-Lys631) (O00206-1) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Apoptosis |Intracellular | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | TLR4, also known as TLR-4, is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family, which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. TLR4 is most abundantly expressed in placenta, and in myelomonocytic subpopulation of the leukocytes. TLR 4 has also been designated as CD284 (cluster of differentiation 284). It has been implicated in signal transduction events induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) found in most gram-negative bacteria. TLR4 Cooperates with LY96 and CD14 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). It acts via MYD88, TIRAP and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. It is also involved in LPS-independent inflammatory responses triggered by Ni(2+). |
| Reference |
