Human TNFRSF25 / DR3 / TNFRSF12 Protein (Fc Tag)
APO-3,DDR3,DR3,LARD,TNFRSF12,TR3,TRAMP,WSL-1,WSL-LR
- 100ug (NPP4326) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12095-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | APO-3,DDR3,DR3,LARD,TNFRSF12,TR3,TRAMP,WSL-1,WSL-LR |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human TNFRSF25/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer consists of 416 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 46 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rhTNFRSF25/Fc monomer migrates as an approximately 55 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 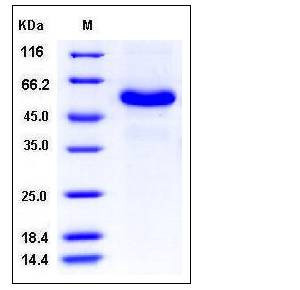 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human TNFRSF25 (NP_003781.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Gln 199) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Cytokines / Chemokines in Angiogenesis |TNF Superfamily |Processes Regulated by TNF Superfamily Members | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 25 (TNFRSF25), also known as Death receptor 3 (DR3) or TNFRSF12 is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor is expressed preferentially in the tissues enriched in lymphocytes, and it may play a role in regulating lymphocyte homeostasis. TNFRSF25/DR3/TNFRSF12 has been shown to stimulate NF-kappa B activity and regulate cell apoptosis. The signal transduction of this receptor is mediated by various death domain containing adaptor proteins. Knockout studies in mice suggested the role of this gene in the removal of self-reactive T cells in the thymus. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene encoding distinct isoforms have been reported, most of which are potentially secreted molecules. The alternative splicing of this TNFRSF25 encoding gene in B and T cells encounters a programmed change upon T-cell activation, which predominantly produces full-length, membrane bound isoforms, and is thought to be involved in controlling lymphocyte proliferation induced by T-cell activation. |
| Reference |
