Human TNFRSF4 / OX40 / CD134 Protein (His & Fc Tag)
ACT35,CD134,IMD16,OX40,TXGP1L
- 100ug (NPP1679) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10481-H03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ACT35,CD134,IMD16,OX40,TXGP1L |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human TNFRSF4/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer after removal of the signal peptide. The reduced monomer consists of 436 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 48.2 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh TNFRSF4/Fc monomer is approximately 68 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Leu 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 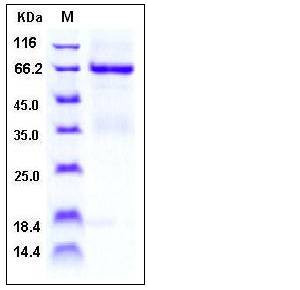 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Ala 216) of human TNFRSF4 (NP_003318.1) precursor was fused with the C-terminal polyhistidine-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Immobilized Cynomolgus mFc-TNFSF4 (P90088-C04H) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human TNFRSF4-Fch, The EC50 of human TNFRSF4-Fch is 0.23-0.55 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cluster of Differentiation (CD) |B Cell CD Antigen |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | OX40 (CD134) and its binding partner, OX40L (CD252), are members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor/tumor necrosis factor superfamily, is known to break an existing state of tolerance in malignancies, leading to a reactivation of antitumor immunity. The interaction between OX40 and OX40L plays an important role in antigen-specific T-cell expansion and survival. OX40 and OX40L also regulate cytokine production from T cells, antigen-presenting cells, natural killer cells, and natural killer T cells, and modulate cytokine receptor signaling. In line with these important modulatory functions, OX40-OX40L interactions have been found to play a central role in the development of multiple inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, making them attractive candidates for intervention in the clinic. Conversely, stimulating OX40 has shown it to be a candidate for therapeutic immunization strategies for cancer and infectious disease. |
| Reference |
