Human TSPAN1 Protein (aa 110-211, Fc Tag)
TSPAN1
- 100ug (NPP2561) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13073-H15H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | TSPAN1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human TSPAN1 comprises 351 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 39.1 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 43-53 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ser |
| SDS-PAGE | 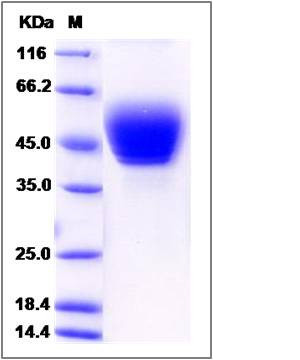 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human TSPAN1 (O60635)(Tyr110-Asn211) was expressed with the Fc region of rabbit IgG at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Trafficking |Vesicle Transport |Adapters |Transmembrane | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | TSPAN1 belongs to the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Tetraspanins have four hydrophobic domains, intracellular N- and C-termini and two extracellular domains. Tetraspanins act as scaffolding proteins, anchoring multiple proteins to one area of the cell membrane. They also mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. TSPAN1 interacts with human thiamine transporter-1 (hTHTR-1). HTHTR-1 contributes to intestinal thiamine uptake, and its function is regulated at both the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. TSPAN1 and hTHTR-1 colocalize in human intestinal epithelial HuTu-80 cells. Coexpression of TSPAN1 in these cells led to a significant decrease in the rate of degradation of hTHTR-1 compared with cells expressing the hTHTR-1 alone; in fact the half-life of the TSPAN1 protein was twice longer in the former cell type compared with the latter cell type. |
| Reference |
