Human UBE2D4 Protein (His Tag)
HBUCE1
- 100ug (NPP4361) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13204-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | HBUCE1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human UBE2D4 consisting of 162 amino acids and migrates as an approximately 18.5 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 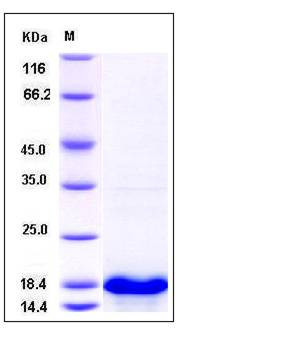 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human UBE2D4 (Q9Y2X8) (Met 1-Met 1474) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Histone Modifying Enzymes |Ubiquitylation |E2 Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzymes |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 0.1M NaCl, 10% glycerol, 2mM DTT, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | UBE2D4 is a member of the ubiquitin-conjugating E2 family whose members perform the second step in the ubiquitination reaction. Initially identified as the main process for protein degradation, ubiquitination is believed nowadays to be crucial for a wider range of cellular processes. The outcome of the ubiquitin-conjugation reaction, and thereby the fate of the substrate, is heavily dependent on the number of ubiquitin molecules attached and how these ubiquitin molecules are inter-connected. To deal with this complexity and to allow adequate ubiquitination in time and space, a highly sophisticated conjugation machinery has been developed. In a sequential manner, ubiquitin becomes activated by an ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1), which then transfers the ubiquitin to a group of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s). Next, ubiquitin-loaded E2s are interacting with ubiquitin protein ligases (E3s) and ubiquitin is conjugated to substrates on recruitment by the E3. These three key enzymes are operating in a hierarchical system, wherein two E1s and 35 E2s have been found and hundreds of E3s have been identified in humans. It has been identified the UBE2D family (UBE2D1-4) as E2 partners for IDOL that support both autoubiquitination and IDOL-dependent ubiquitination of the LDLR in a cell-free system. |
| Reference |
