Human ULBP1 / N2DL1 Protein (His Tag)
RAET1I
- 100ug (NPP4369) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10679-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | RAET1I |
| Molecular Weight | The mature form of recombinant human ULBP1 comprises 202 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 23.8 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rhULBP1 is approximately 28-32 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gly 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 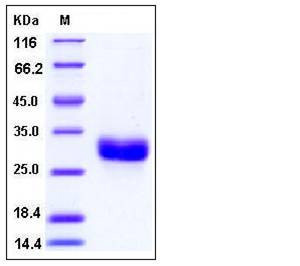 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human ULBP1 (NP_079494.1) (Met 1-Gly 216) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Immobilized human ULBP1-His (P10679-H08H) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human S4-Fc3L3-NKG2D (P10575-H01S), The EC50 of human S4-Fc3L3-NKG2D (P10575-H01S) is 0.39-0.91 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Signaling Pathway |Representative pathway |TLR Signaling pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | UL16-binding proteins (ULBP) or retinoic acid early transcripts-1 (RAET1) are ligands to the activating receptor, NKG2D. Ten members of the human ULBP/RAET1 gene family have been identified to encode for potentially functional proteins, and have tissue-specific expressions. ULBP1, also known as RAET1I and NKG2DL1, together with at least ULBP 2 and 3, are well-known ligands for NKG2D, and activate multiple signaling pathways in primary NK cells, resulting in the production of cytokines and chemokines. ULBP1 is expressed in T-cells, B-cells, erythroleukemia cell lines and in a wide range of tissues including heart, brain, lung, liver and bone marrow, as well as some tumor cells. As an unconventional member of the MHC class I family, ULBP1 function in immune responses, especially in cancer and infectious diseases. Unlike other ULBP members, ULBP1 is able to interact with soluble CMV glycoprotein UL16 in CMV infected cells. The interaction with UL16 blocked the interaction with the NKG2D receptor, and thus might escape the immune surveillance. Furthermore, UL16 also causes ULBP1 to be retained in the ER and cis-Golgi apparatus so that it does not reach the cell surface. The ULBP1 regulation may have implications for development of new therapeutic strategies against cancer cells. |
| Reference | 1. Rölle, A. et al., 2003, J Immunol. 171(2): 902-908. 2. López-Soto, A. et al., 2006, J Biol Chem. 281(41): 30419-30430. 3. Song, H. et al., 2006, Cell Immunol. 239(1): 22-30. 4. Eisele, G. et al., 2006, Brain. 129 (9): 2416-2425. 5. Romphruk, AV. et al., 2009, Immunogenetics. 61(9): 611-617. 6. Sutherland, C.L. et. al., 2002, J. Immunol. 168: 671-679. |
